Wherever you are in your journey of SEO expertise, whether you are starting at the beginning or if you’re looking for ways to achieve advanced outcomes, it's important to have a grasp on the nuts and bolts of how internal links work and how to use them to reach your goals.
Internal links originate from your own site and point to other pages on your site. You can learn more about them at our cheat sheet to internal linking: The Ultimate Cheat Sheet on Internal Link Analysis for SEO.
They shouldn't be confused with external links!
Crawling, indexing, and ranking happen first and foremost with internal links.
The Goals of Internal Linking
The goals of internal linking are simple:
- Provide clear navigation for the user on your website
- Define the architecture and hierarchy of your website
- Distribute page authority and ranking power throughout the site
- Improve how the site is indexed and crawled
The way many websites are organized today is great for people who are looking to find products, but it’s not ideal for SEO. Site taxonomy, or your site's classification of its pages, includes a first level of navigation links, usually in the main menu or navigation bar prominently featured on the home page.
Most of the time a website is organized around generalized sections or topics in navigation links and it filters down into smaller categories.
This process is great for people who are looking to find something that falls into those categories, but tougher for web crawlers that are indexing your site. The problem exists due to the tree architecture and website structures that filter from general to specific topics.
Many website structures navigate according to these paths to different pages. However, the average user or casual visitor on your site will only go through seven clicks from beyond the home page.
The goal with internal linking is to get customers, visitors to your website, and search engines to understand where they need to go with as few clicks as possible. As a result, a good SEO strategy for internal links has to take into account these two schools of thought.
Recommended Reading: 7 Benefits of Internal Linking in SEO
Controlling What Links and Pages Are Crawled
Make sure you only allow search engines to go where you want them to go by following these recommendations for your whole site, specific pages, and specific links.
We can do this by putting up signs that are akin to “Stop! Danger! Do not enter!” Even if you have a signpost there, you still can strongly suggest not going to a certain part of your site. Here are a few different ways you can control that:
Site Wide
In this case, you would instruct the search engines never to go to a certain section of your site - no matter what. To do this, you can add instructions into your robots.txt file.
For example, if you have a URL that ends in /apparel and you want to override any possibility of that page being accessed, you can include a disallow*/apparel in your robots.txt (translation: do not allow any user agent, indicated by the asterisk, to access any URL that contains /apparel). This works nearly every time it's applied.
Page Specific
Here, we want to tell whoever lands on the page that there is nothing to see. We can do that with a meta name robots tag that looks like this:
<meta name="robots" content="nofollow,noindex"/>
In other words, this prevents the links on the page in question from being followed or indexed. Generally speaking, search engines will follow this instruction.
Link Specific
You can also put a tag on the links themselves that tells a search engine not to follow a link. You do this by adding a Rel=nofollow directive to the link, which looks like:
<a href=https://www.example.com/apparel”rel=nofollow/>
This is done in situations where the content is not related or is possibly incorrect and serves as more of a recommendation to the search engine. Your best bet is to apply a Site Wide instruction as listed above.
How Does seoClarity Help?
We store a complete internal link graph of your entire website with every crawl using our proprietary crawler. This stores the relationship for every page that links to another and it also stores the anchor text used to link to a page. Using Internal Links Analysis, it’s easy to set up a new crawl to do an audit project.
To do this, we visit the Advanced Settings feature in Clarity Audits Projects. We set up a new crawl and select the Internal Links Analysis option, which will generate a link graph of the links found on the site.
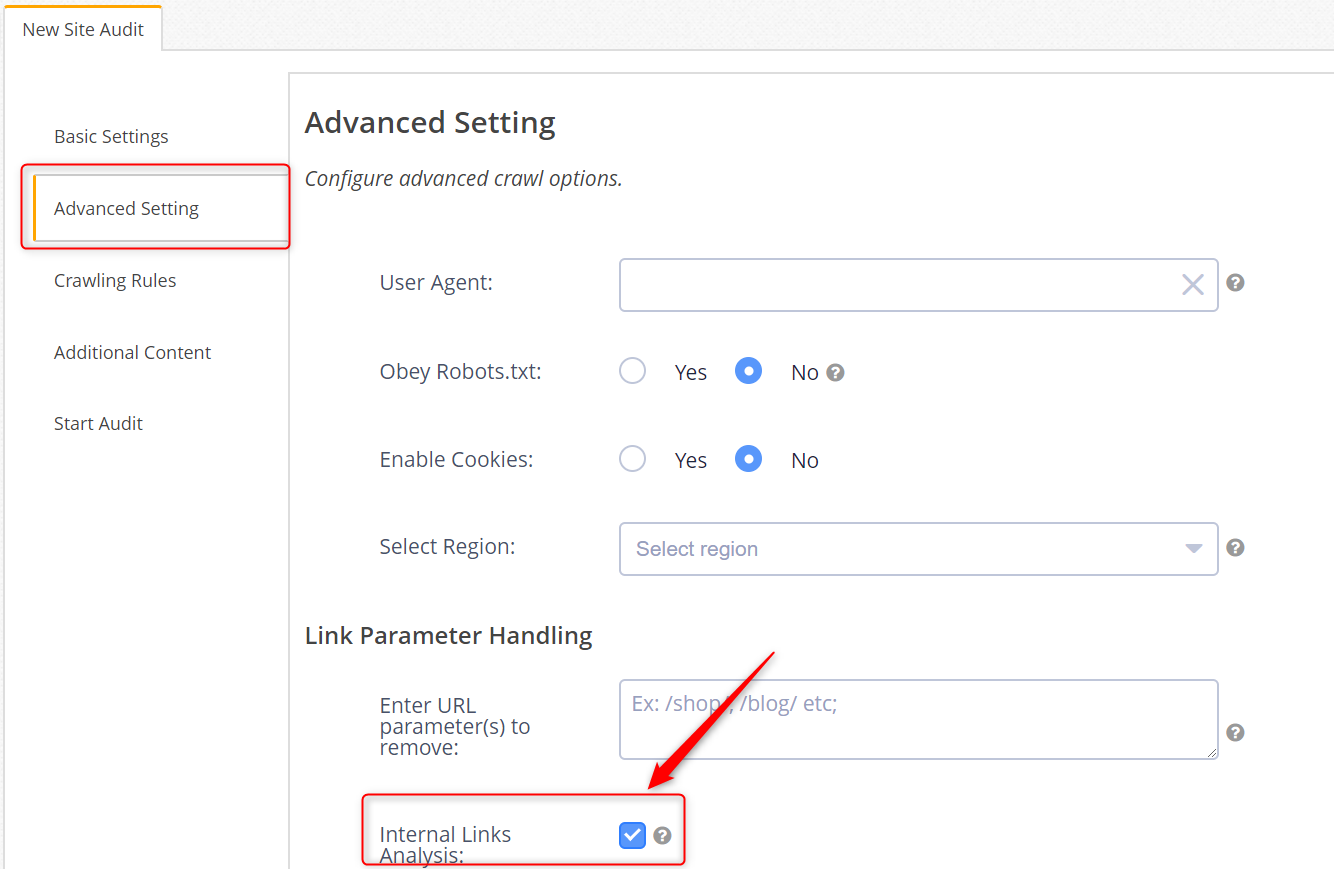
This can be analyzed in the internal links analysis feature for more detailed insights into internal link structure optimization, including:
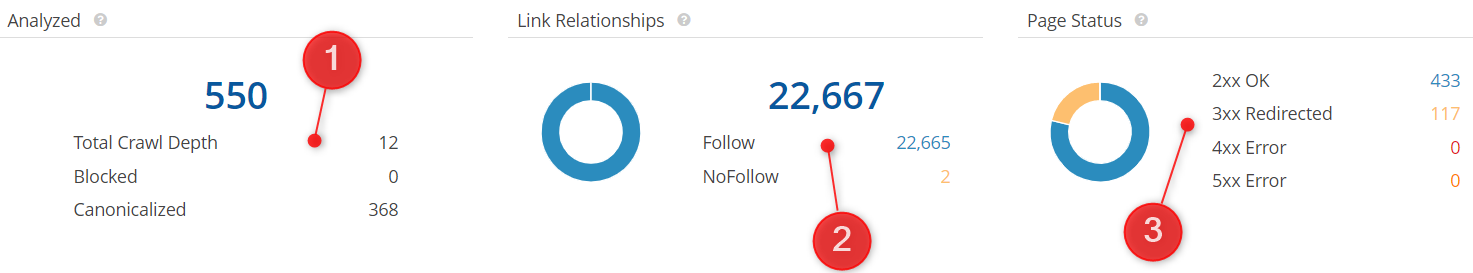
- Count of URLs analyzed, the total crawl depth, count of URLs blocked from crawling and count of URLs crawled with a canonical
- Number of internal links, broken down based on Follow or NoFollow directives
- Summary of response codes for 2xx, 3xx, 4xx, and 5xx statuses based on the analyzed URLs
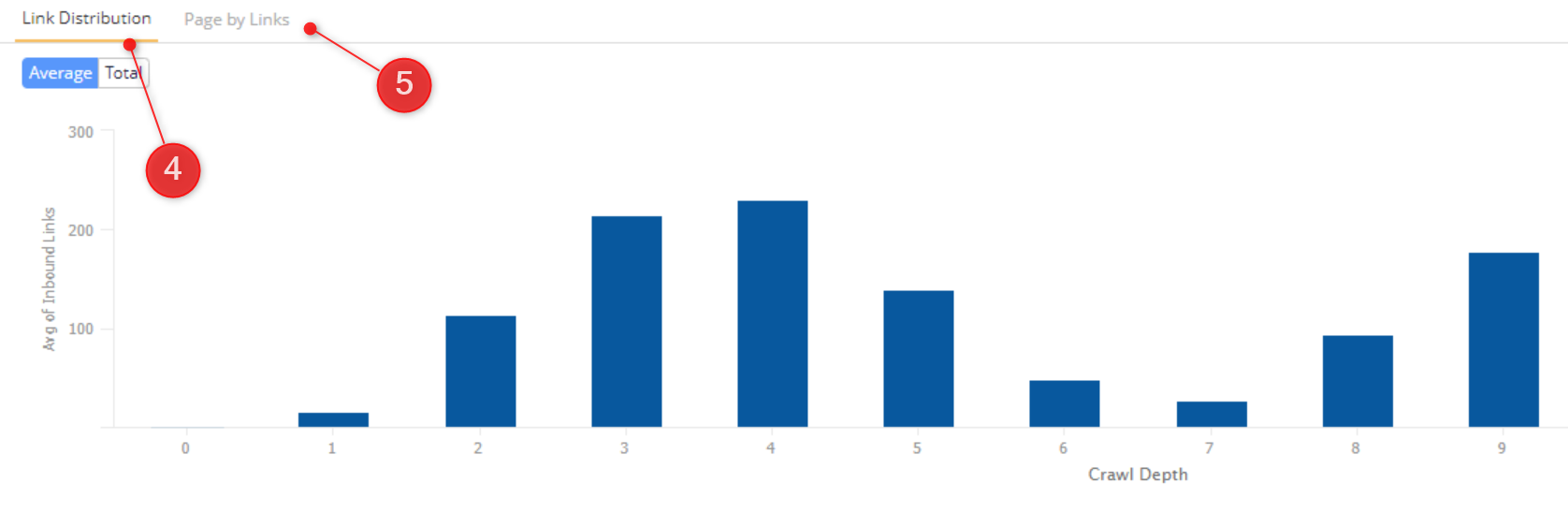
- Average or total number of links by crawl depth (depth can be thought of as the number of links away from the starting URL).
- Number of pages based on count of inbound links.
In order to be effective, you want a clean, broad crawl. If your site has a million pages, then there are many millions of link relationships.
If your website has a million pages and you only crawl ten thousand, you’re not going to have a full view of all of the signposts. That’s why the broader you can go with a crawl, the greater visibility you’ll have into your signposts and what they are saying.
The internal link graph display shows every internal link found in the crawl, but do note however, that only the top million pages with the MOST links are displayed.
You can also do a quick audit of the keywords that point to your most important pages. Ultimately, you want to make sure the keywords are relevant and mostly the same that point to a particular page.
Optimizing Your Site's Internal Link Structure At Scale
In addition to providing insightful internal link analysis, seoClarity offers a solution to optimizing your internal link structure at scale by automatically creating internal links for thousands of pages.
ClarityAutomate Link Seeker surfaces pages buried deep in your site's hierarchy to increase the discoverability of valuable pages—all without the help of a dev team.
In addition, it also uses sophisticated AI technology and natural language processing to automatically determine the best target pages and the pages that should link to them but currently do not.
As the only front-to-end automated internal linking solution, Link Seeker also tracks the performance of all newly created links.
We've already discussed the importance of control when it comes to optimizing your site's internal link structure. That's why Link Seeker allows users to review, approve, modify, and even train the algorithm on what pages to prioritize and which to block.
Final Thoughts
How you decide to organize your website navigation, categories, and various web pages has a hand in determining the best internal link strategy for your company’s SEO success.
When you know more about internal links and how they work, it becomes simple to formulate the right plan of action to optimize the ease and speed in which things are located on your site for site visitors, current customers and online web crawlers, all of whom are looking for specific things in different ways.
When you can correct errors in your internal links to better reflect your priorities and do some proofreading to ensure you don’t have broken links or repetition, your results will be worth the effort.




.png?width=140&name=Untitled%20design%20(10).png)



1 Comment
Click here to read/write comments