For anyone involved in content creation, it's important to consider the implications that duplicate content can have on your site.
While this seems like a straightforward principle on the surface, there are actually quite a few considerations to address when it comes to duplicate content and SEO.
This piece addresses everything you need to consider in addressing duplicate content, when it should be avoided or allowed, and how to address it at scale using an SEO platform.
Table of Contents:
What is Duplicate Content?
Google doesn't give a mathematically precise definition of duplicate content, only saying that it refers to blocks of content that are identical or "appreciably similar" to other online content.
It can occur intentionally when other sites try to steal your content and republish it as their own or, in many cases, you can accidentally create duplicate content on your own site.
For example, displaying the same product description across various pages for different variants of the same item is a form of duplicate content. We'll go into more detail on the many potential causes of duplicate content a little later.
Is Duplicate Content Plagiarism?
Plagiarism and duplicate content overlap but have different meanings.
Plagiarism is a legal term involving the theft of intellectual property. If you publish something created by someone else without permission, you can be liable for legal and civil penalties. This is why there are plenty of tools that can scan for and check plagiarism.
Duplicate content, on the other hand, is an SEO issue, not a legal issue. Google can't fine or imprison you, but its algorithm does determine your site's ability to rank. Google rewards content that it regards as useful and authoritative. The more original your content is, the more likely it is to fit these criteria.
Duplicate Content vs Article Spinning
Some people rewrite or "spin" articles to make them original. This can either be done manually or with the help of software. AI-powered article spinners are usually programmed to make content at least 80% unique.
This approach, however, can be quite misleading. For one thing, uniqueness certainly doesn't equate to high quality. Article spinning software generally produces gibberish or, at best, barely passable articles.
Furthermore, when it comes to plagiarism, you're not allowed to use even a single sentence of someone else's work without permission. An article could be 98% unique and still plagiarized. It's best to aim for 100% uniqueness.
Rewriting or spinning content is not a winning strategy if you're aiming to brand yourself as an authority in your space. Plus, with those plagiarism checks, it's best to err on the side of cation and avoid any legal issues.
Different Types of Duplicate Content
Duplicate content comes in many different forms. Here are some of the most common types of duplicate content:
- Content that is simply taken from one site and republished on another. If this is done without permission, it's also plagiarism. Even if you have permission, the content is still duplicated.
- On-site duplication. Items you publish yourself across multiple pages. In some cases, you may do this deliberately, like publishing a blog post or video on one page of your website as well as others, but these do constitute duplicate pages. Longer content pieces like blog posts aren't the only thing that can be duplicated. Similar or identical meta descriptions are also duplicative.
- Content that's not identical to but very similar to another piece. This is where it gets tricky, as you may consider something unique if it's not a direct match to another item. But, for example, if you paraphrase a source using very similar language, you may be slipping into the duplicate content category. Going back to the example we mentioned earlier, product descriptions with just slight wording changes may also fall into this category.
Potential Causes of Duplicate Content
Looking beyond content itself, there are several technical issues that can slyly generate duplicate content:
- URL Parameters. These occur when applying URL parameters or tracking in your code. According to Google, these URL variations are made by creating a key and a value separated by an equals sign and joined by an ampersand. So, while the URLs may appear different, the user arrives at the same page no matter the link they click.
- Session IDs. Similar to applied URL parameters, session IDs occur when a different ID within the URL is given to every user that visits your site.
- Different Versions of Your Site. This applies to sites that have both a www.example.com and example.com version of their pages. This also occurs for sites that have an SSL certificate and maintain both the HTTP and HTTPS versions of their site.
- Faceted Navigation. Faceted, or filtered navigation, helps users filter details on your site to discover the information they seek, allowing them to customize their search experience. The search engine, however, may consider these filtered URL results to be duplicate content.
Recommended Reading: Pagination vs. Infinite Scroll: What's the Difference?
All of these issues, whether apparent in the content or hidden within your URL, have the potential to impact your traffic to your target pages.
Common Misconceptions About Duplicate Content
Myth 1: Content Syndication Leads to Duplicate Content Issues
Contrary to popular belief, content syndication does not necessarily result in duplicate content issues.
Content syndication refers to the process of deliberately republishing content from another source with credit and permission (so it's not plagiarized content). Many authoritative websites, such as Huffington Post and Buzzfeed, are built on syndicating articles from other sites.
While it's true that syndicating your content on other websites can potentially lead to duplicate versions of your content appearing across the web, search engines are well-equipped to handle this.
They have sophisticated algorithms in place to recognize and differentiate between original and syndicated content. As long as you follow best practices, such as using canonical tags and providing proper attribution, content syndication can be a valuable strategy for increasing your reach and driving traffic to your website.
Myth 2: Search Engines Have Duplicate Content Penalties
Contrary to popular belief, search engines do not impose penalties for duplicate content. Instead, they strive to provide the best user experience by displaying the most relevant and authoritative content in search results.
However, even if there is no direct content penalty from Google, that doesn't mean duplicate content doesn't negatively impact your SEO. It can still impact your website's visibility and rankings.
Let's dive into some of the effects duplicate content can have on SEO.
The Effects of Duplicate Content on SEO
So, just how bad is duplicate content from an SEO perspective? Here are a few of the potential disadvantages:
- Google will usually only display one version when there is similar content. It's harder to rank for content that's not distinctive. If you're competing with larger, more established sites, your own content will likely rank much lower in search results.
- It reduces the effectiveness of backlinks. If near-identical content can be found at different URLs, you're competing with each of these sites for backlinks. Providing unique value in your content is the key to standing out and earning more links.
- Your audience is less likely to click on your site. When multiple versions of the same (or a very similar sounding) item are displayed in search results, users are likely to choose one and ignore the other. When your content stands out, it's more likely people will click on it, as they can expect something new.
- Duplicate content on your own website can be confusing to Google. Confusing Google's crawler with duplicate content can lead to less effective indexing and, consequently, a lower search ranking.
- It dilutes your brand. Unless your business is built on the curation model, it's advantageous to brand yourself with unique content that reflects your own ideas and style
5 Ways to Prevent Duplicate Content On Your Site
Now that you know the potential downsides of having duplicate content on your site, here are some effective ways to prevent it from happening.
1. Prioritize Creating Original Content
There are several factors to keep in mind to ensure that your content is original.
- If you outsource content creation, make sure you're using a trustworthy source. There are cases in which freelancers will send you "original" articles that turn out to be plagiarized.
- When doing research, be careful about quoting or paraphrasing. Sometimes, you can unconsciously copy someone else's words. Quoting people is fine, but if you overdo it, this will detract from the uniqueness. When researching, use multiple sources.
- Be mindful when including information from other websites. Rather than quoting long passages or asking permission to republish the whole piece, you can always just insert a link to the original piece.
- Always employ human review when creating AI-generated content. Depending on the input data, how much information the model has been fed on the topic, and the parameters you've set for the AI model you're using, it's possible for AI-generated outputs to be similar to other published content. To avoid any duplicate content issues, avoid simply copying and pasting large portions of AI-generated text. Instead, make sure the content is human-reviewed and edited to add your own unique brand knowledge, tone, and opinions.
Struggling to come up with unique content ideas? Here's how to get the best SEO content ideas directly from your audience.
2. Monitor and Regularly Audit Website Content
It's a good idea to perform an SEO content analysis for all your content. This will help you identify not only duplicate content but any other SEO issues that need addressing.
To prevent duplicate content from going unnoticed, here are some of the many ways to identify duplicate content on your site.
- Use a plagiarism checker such as Copyscape to test the uniqueness of your content.
- Place text into the Google search bar. This is a good way to spot duplicate content within your own pages and also lets you know if anyone else has taken your content without authorization.
- Use an advanced tool such as the Content Similarity Checker (Simcheck), one of the SEO content analysis tools offered by seoClarity. This tool allows you to compare the content between web pages to check for similarity by simply uploading an XLS, CSV, or TXT file. This provides a simple way to get a precise summary of similarity percentages between pages. While you can perform manual searches to identify duplicate content, using an SEO platform makes the process scalable for content teams that need to check large numbers of pages.
For seoClarity Clients, navigate here to Content Similarity Checker in the platform.
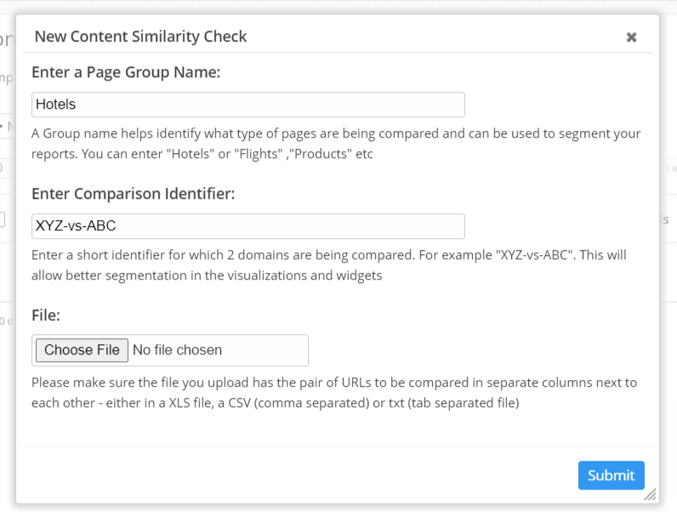
3. Fix Duplicate Content With Tags
There are several actions you can take to reduce duplicate content. Two of the best methods are 301 redirects and canonical tags. These instruct the search engines to index a specific URL.
- 301 redirects. When users can reach your site using different URLs, a 301 redirect will send traffic to the URL you prefer. This ensures that Google doesn't get confused and consider the separate URLs as two distinct websites.
- Canonical tags. A canonical URL is another name for your preferred URL, the one you want the search engines to rank. A Rel=Canonical tag is particularly useful when you have product pages with many variations that create distinct URLs. For example, if you sell shirts that come in different sizes and colors, Google may assume that each variation is a separate page if you don't specify canonical tags.
- Noindex tags. Use the noindex tag if you don't want a certain page containing duplicate content to appear in search results.
Recommended Reading: 12 Common Hreflang Mistakes and How to Prevent Them
4. Remove, Consolidate, or Edit Your Content
After auditing your existing content, you may decide to remove pages that are too similar to others or consolidate them together into one piece.
Another option is to make changes to the content to enhance its uniqueness. You might focus on different long-tail keywords so your pieces discuss similar topics using distinct language. If you have very similar pages (e.g. product pages, pages for different locations), it's worth taking the time to reword them.
For example, a real estate company may have many pages for different locations, with only the location names changed. You could change the wording to make the entire page unique.
5. Stop Content Theft
Content thieves, also known as content scrapers, are unscrupulous publishers who simply steal others' content without asking permission or giving credit to the source.
On the vast web, this practice is quite common, but you don't want your content republished on random, low-quality sites.
That's why it's important to monitor the internet for content scraping. Here are some effective ways to do so:
- Use Google Alerts to monitor the web for mentions of your brand or products.
- If you use WordPress, you can use a plugin such as Copyright Proof to prevent theft of your images.
- Use a plagiarism detector to check for anyone copying content from your website. Copyscape offers a paid service that sends out plagiarism alerts.
- If you are aware of someone stealing your content, file a DMCA takedown notice.
Conclusion
As a content creator, you should know as much about your content as possible. This includes understanding the difference between duplicate and original content, and the implications both bring to SEO.
As we discussed, this doesn't mean that everything has to be unique. You may want to republish or curate certain items. To brand yourself and rank better in the search engines, however, it's to your advantage to publish mostly unique content.
<<Editor's Note: This post was originally published in November 2020 and has since been updated.>>



.png?width=140&name=Untitled%20design%20(10).png)


Comments
Currently, there are no comments. Be the first to post one!